 |
|
|
|
|
| Map Gallery Slide Show | Image 52 of 75 | Saratoga Bedrock Geology - Type 2 |
 |
||
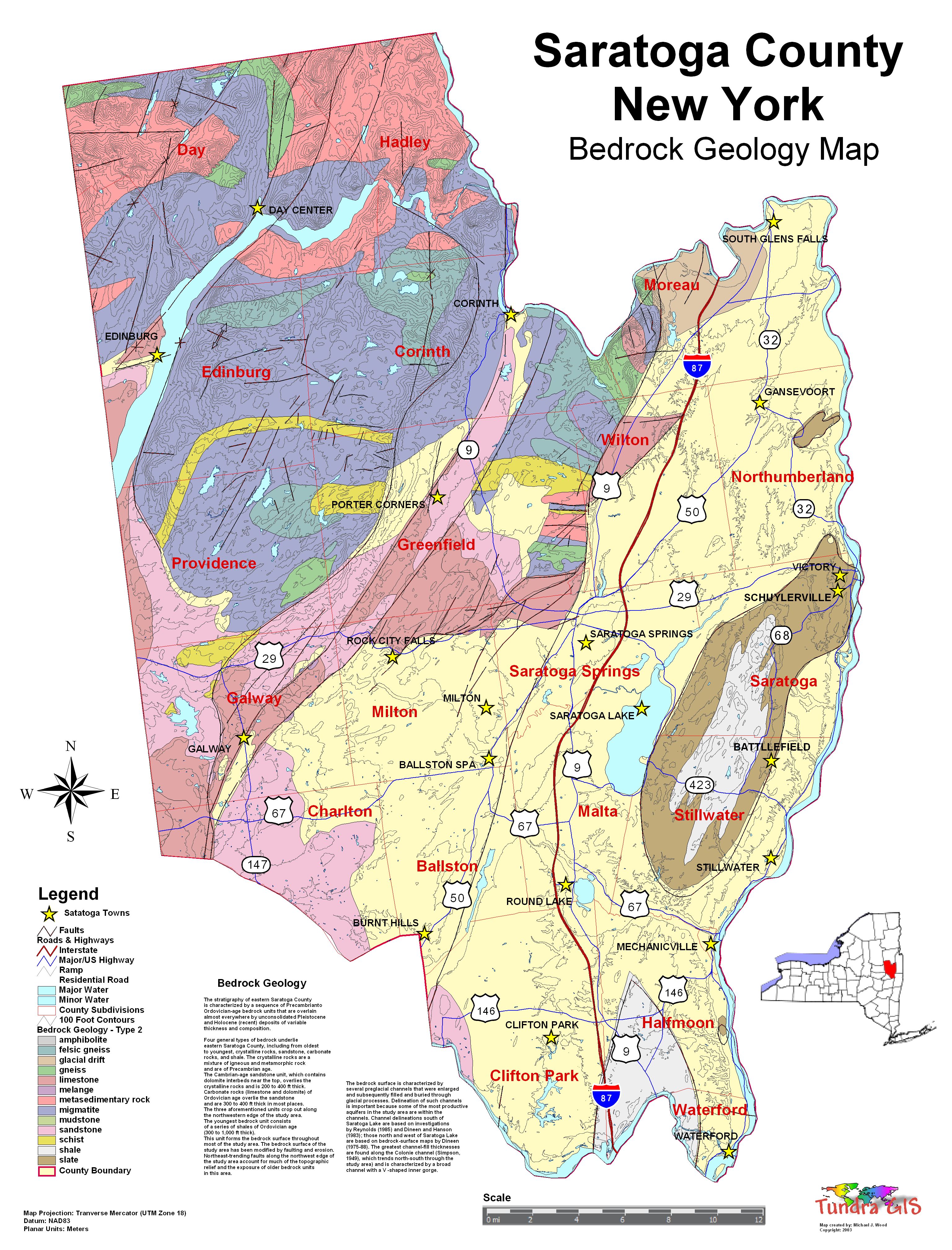
| Saratoga County, New York Bedrock Geology Map (Rock Type 2) Bedrock Four general types of bedrock underlie eastern Saratoga County, including from oldest to youngest, crystalline rocks, sandstone, carbonate rocks, and shale (Heath, 1963). The crystalline rocks are a mixture of igneous and metamorphic rock and are of Precambrian age. The Cambrian-age sandstone unit, which contains dolomite interbeds near the top, overlies the crystalline rocks and is 200 to 400 ft thick (Heath, 1963). Carbonate rocks (limestone and dolomite) of Ordovician age overlie the sandstone and are 300 to 400 ft thick in most places (Heath, 1963). The three aforementioned units crop out along the northwestern edge of the study area. The youngest bedrock unit consists of a series of shales of Ordovician age (300 to 1,000 ft thick). This unit forms the bedrock surface throughout most of the study area (Heath, 1963). The bedrock surface of the study area has been modified by faulting and erosion. Northeast-trending faults along the northwest edge of the study area (Heath, 1963) account for much of The topographic relief and the exposure of olderbedrock units in this area. The bedrock surface is characterized by several preglacial channels that were enlarged and subsequently filled and buried through glacial processes. Delineation of such channels is important because some of the most productive aquifers in the study area are within the channels. The thalweg, or deepest course, of each channel is depicted, along with approximate elevations, in plates 1 through 5 and 7. (No buried channels have been identified in the areas shown in plates 6 and 8.) Channel delineations south of Saratoga Lake are based on investigations by Reynolds (1985) and Dineen and Hanson (1983); those north and west of Saratoga Lake are based on bedrock-surface maps by Dineen (1975-88). The greatest channel-fill thicknesses are found along the Colonie channel (Simpson, 1949), which trends north-south through the study area (pls. 1-3, 5, and 7) and is characterized by a broad channel with a V -shaped inner gorge (Dineen and Hanson, 1983). WHAT IS A GEOLOGIC MAP? CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD |
||
| < back | up ^ | next > |